>Colour Wheel
The colour wheel is useful when trying to find colours that are similar in a sense that they can come across asthetically pleasing.
>Analog Colours
Analog colours have colours that are adjacent to them on the colour wheel, one of the colours is the most dominant while the other is used to almost compliment the initial colour.
>Complementary Colours
These colours consist of two which are opposite eachother on the colour wheel, it looks best placed when to fairly opposite personality colour are put together e.g warm and cool colours like red and blue.
>Split Complementary Colours
Split complementary is a variation of the standard complementary scheme. This theme uses a colour then two adjecent colours to create a complimentary effect, provding high contrast without strong tension.
>Triad Colours
Triad colours uses three colours equally spaced around the colour wheel. It is a quite popular concept offering large amounts of contrast without seeming out of place. It is meant to look more balanced and harmonious.




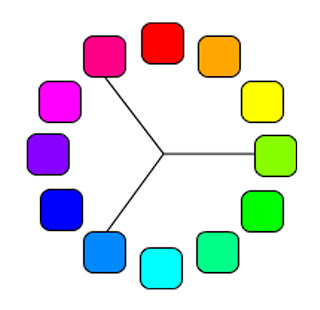
Hi Antony, just curious if you realized that you used two different color wheels above -- the first is a RYB color wheel (pigment color), and the second is a RGB color wheel (light color). My students saw the error and wanted you to know.
ReplyDeleteThanks, and good luck.